Work Smart not Hard: The Effect of Ultradian Rhythms on Learning

Have you ever noticed how your energy levels, mood, and cognitive performance tend to fluctuate throughout the day? These fluctuations are not just random; they are part of our body's natural rhythm known as the ultradian rhythm. This rhythm is a biological cycle that lasts less than 24 hours and affects many aspects of our physical and mental functioning, including learning and memory consolidation.
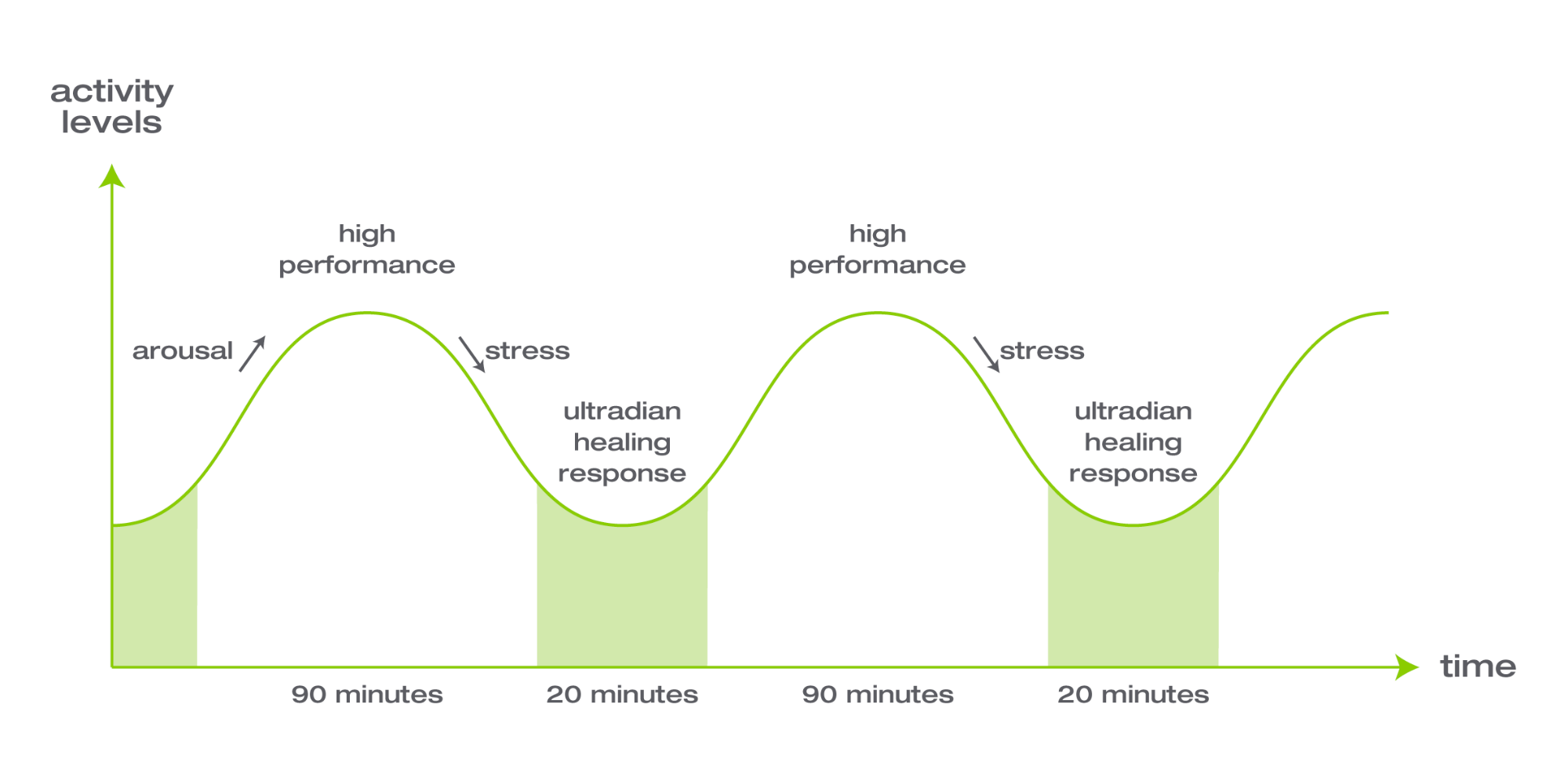
Research suggests that taking breaks during study or work sessions that align with these natural cycles can help improve concentration, creativity, and overall cognitive performance. For example, taking a 20-30 minute break every 90 minutes can help to recharge your brain and improve your ability to learn and retain new information. This approach is often referred to as the "Pomodoro technique" and is a popular time-management strategy used by many students and professionals.
The Pomodoro technique is based on the principle that the brain can only focus on a task for a certain amount of time before it begins to tire and lose efficiency. By taking regular breaks, the brain is given a chance to rest and recover, allowing you to maintain optimal cognitive performance throughout the day. These breaks are not only good for the brain but can also help reduce stress and prevent burnout.
But why does this approach work so well? It all comes down to the brain's natural ultradian rhythm. Studies have shown that the brain goes through cycles of activity and rest, with each cycle lasting approximately 90 minutes. During this time, the brain is active and engaged, and then it needs to rest to recharge its batteries. This cycle is repeated throughout the day, with the intensity of brain activity and rest periods varying throughout the cycle.
The brain's ability to learn and retain information is closely linked to this natural rhythm. During the rest period, the brain consolidates newly acquired information and strengthens memory formation. This process is essential for effective learning, and regular breaks that coincide with the natural ultradian rhythm can help improve memory consolidation.
It's important to note that the specific effects of ultradian rhythms on learning can vary from person to person and may depend on factors such as sleep quality, stress levels, and overall health. Some people may find that shorter or longer break intervals work better for them, or that their natural ultradian rhythm differs from the 90-minute cycle. The key is to pay attention to your body's natural signals and find a routine that works best for you.
In conclusion, the ultradian rhythm plays an important role in our body's natural functioning, including learning and memory consolidation. Taking regular breaks during study or work sessions that align with this natural rhythm can help improve cognitive performance and prevent burnout. By understanding the natural rhythm of our bodies, we can optimize our learning and work habits to achieve greater productivity and success.